
In Human Anatomy Atlas, the fascia displays as part of the muscular system. Thin layers of fascia surround our internal organs, as well as muscles, groups of muscles, blood vessels, and nerves, holding them in place or allowing them to slide past each other as needed.įascia of the thighs with nerves and blood vessels. Image from Human Anatomy Atlas.įascia might not get as much publicity as ligaments or tendons, but it’s just as important. You might already be familiar with a few important instances of fascia in the body such as the iliotibial (IT) band, which runs along the outside of the thigh and stabilizes the knee, or the plantar fascia, which runs along the bottom of the foot and connects the heel bone to the toes. Īt the most basic level, fascia is a type of connective tissue. To get you hyped for this new content, we’ll talk in this blog post about what fascia and fascial compartments are, and we’ll also give a brief overview of some common pathologies that affect them.įascia of the right arm. Guess what, VB Blog readers? We have some exciting news for you! Fascial compartments have been one of our most-requested anatomy additions, and we've added them to Human Anatomy Atlas 2021 and Human Anatomy Atlas for Web Suite and Courseware! In persistent or severe cases the best solution is usually to operate by releasing the sheath and allowing the muscle to expand naturally.New Anatomy Content: Fascia, Fascial Compartments, and Compartment Syndrome Sports massage techniques to stretch the muscle sheath may have some success.Ĭross friction massage applied to the sheath may help stretch it and allow more room for the muscle within to function. What can a specialist or doctor do?Ī doctor may prescribe anti-inflammatory medication such as ibuprofen. If compartment syndrome is diagnosed then an extended period of rest in conjunction with correction of foot biomechanics may be required to allow the overdeveloped muscle to atrophy and the sheath to accommodate it. See a specialist to confirm your problem as the injury may just be a chronic muscle strain that has not been allowed to heal properly. The causes of this can be training too much too quickly but you can also be more prone to this if you have laxity in your ankle ligaments for example after severe or recurrent ankle sprains.īiomechanical problems of the foot such as overpronation or over supination may also contribute to the load on the muscle increasing the chance of a chronic compartment syndrome.
After a period of rest, the pain disappears only to come back when the athlete tries to run again. Symptoms include pain which gradually comes on during a run, getting worse until it is impossible to continue. It occurs because the muscle has grown too big too quickly for the sheath that surrounds it. Lateral compartment syndrome mainly occurs in runners. In severe cases, a surgeon can operate to surgically decompress the compartment. They may apply ultrasound or other electrotherapy techniques to help swelling dissipate.Ī doctor may prescribe anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen to reduce pain and inflammation.
Lower extremity compartments professional#
What can a sports injury specialist do?Ī professional therapist can perform compartment pressure tests and confirm the diagnosis. Wearing compression support may also help reduce the swelling and support the muscle.
Lower extremity compartments skin#
Ice should not be applied directly to the skin but wrap in a wet tea towel. Work the upper body instead or swim if this can be done pain-free.Īpply ice or cold therapy for 20 minutes every two hours. If it is particularly painful then seek professional medical advice.Īcute compartment syndrome can be a medical emergency as muscle and nerve damage can occur.
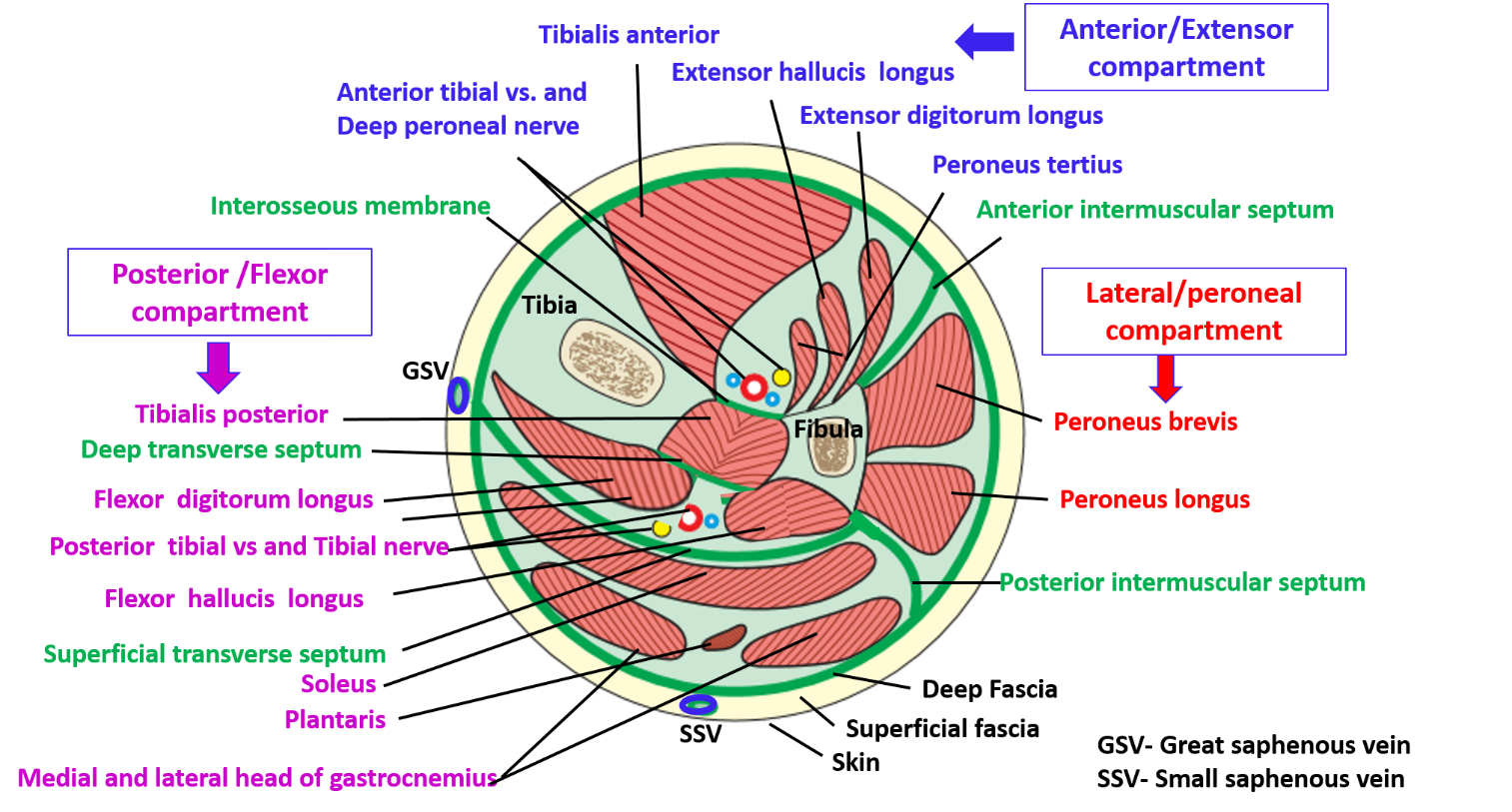
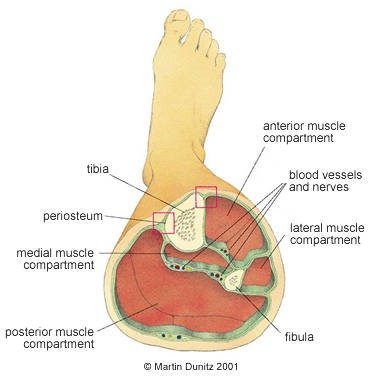
The extra fluid causes too much pressure within the muscle sheath. Acute compartment syndromeĪcute compartment syndrome can occur due to an impact or injury which causes bleeding and swelling within the muscle sheath. Chronic compartment syndrome usually develops gradually over time. Acute compartment syndrome comes on suddenly. Either of which can be the cause of a compartment syndrome.Ĭompartments syndromes are either acute or chronic. The lateral compartment of the lower leg is made up of the peroneus brevis and peroneus longus muscles.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
